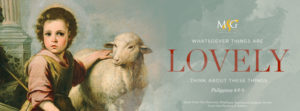The Heavenly Shepherd
Oil on canvas
Bartolomé Esteban Murillo
Spanish, 1617–1682

Click on the links throughout the article to view additional artists’ works and reference material.
The streets of Seville are flooded with disease, poverty, and orphans. A little boy crouches underneath an awning to savor a loaf of bread while a five year old girl walks the streets with a basket of fruit to sell—scenes that could easily find their origin in a descriptive Charles Dickens’ novel.
However, seventeenth-century Spain, though bustling with exciting change, faced the hardships of political uncertainty and devastating plagues. Disease struck homes and left children destitute and alone.
One Baroque artist, Bartolomé Esteban Murillo, saw Sevillian paupers in their miserable state yet painted them in an ideal setting. Unlike his contemporary Jusepe de Ribera, who filled his works with suffering and darkness, Murillo chose to display a more peaceful tone in his religious and genre paintings. His works display an idealized image of the poor commoners who lined the streets of Spain.
Born in Seville, Murillo matured as an artist under the influence of fellow Spaniards Zurbarán and Velázquez as well as by viewing art by the Baroque greats Caravaggio, Peter Paul Rubens and Anthony Van Dyck. Although not as popular today, Murillo maintained a prosperous and successful career throughout his lifetime not only in Spain but also across Europe. At one point, the king of Spain halted export of Murillo’s work to keep these valuable treasures within his country’s borders.
M&G displays two of Murillo’s works, The Martyrdom of St. Andrew and The Heavenly Shepherd, both of which offer a somewhat gentle view of their subjects. The Heavenly Shepherd synthesizes the artist’s study of Sevillian street urchins with the time period’s focus on religious art. A similar version of this painting called The Good Shepherd resides in Madrid’s Prado Museum.
In The Heavenly Shepherd, Murillo provokes the viewer with Christ’s arresting gaze to consider the innocent, yet sober young Shepherd, and he subtly references symbols related to the life of Christ:
- The purple robe hails Him as the King of Kings.
- The shepherd’s staff extends as a scepter from Christ’s hand.
- The ominous broken column signifies the broken and brief life of the Good Shepherd.
- The sheep allude to the fold of God, His children.
 By comparison, Murillo’s work seems like a precursor to Philippe de Champaigne’s The Christ of Derision. Rather than an endearing shepherd boy in a pastoral scene, Christ is portrayed as a physically abused, yet determined man. The foreshadowed death in the Murillo painting is about to unfold in the narrative of Champaigne’s portrait. Together both paintings in their own way point to the dark scenes of Christ’s life just prior to Easter morning’s triumph.
By comparison, Murillo’s work seems like a precursor to Philippe de Champaigne’s The Christ of Derision. Rather than an endearing shepherd boy in a pastoral scene, Christ is portrayed as a physically abused, yet determined man. The foreshadowed death in the Murillo painting is about to unfold in the narrative of Champaigne’s portrait. Together both paintings in their own way point to the dark scenes of Christ’s life just prior to Easter morning’s triumph.
The Heavenly Shepherd stands as only one of many creations by Murillo, who remained a coveted artist until his own death—a result of a tragic fall from a painting scaffold. Murillo left behind an artistic legacy that portrayed Biblical characters and the Sevillian paupers in a fresh, tender manner.
Jessi Hargett, Secondary Education Coordinator
Published in 2017